
JWT ——JSON WEB TOKEN
一. JWT介绍
JSON Web Token (JWT)是一个开放标准(RFC 7519),它定义了一种紧凑的、自包含的方式,用于作为JSON对象在各方之间安全地传输信息。该信息可以被验证和信任,因为它是数字签名的。
官网:https://jwt.io/
GitHub上jwt的java客户端:https://github.com/jwtk/jjwt
JWT使用场景
- Authorization (授权) : 这是使用JWT的最常见场景。一旦用户登录,后续每个请求都将包含JWT,允许用户访问该令牌允许的路由、服务和资源。单点登录是现在广泛使用的JWT的一个特性,因为它的开销很小,并且可以轻松地跨域使用。
- Information Exchange (信息交换) : 对于安全的在各方之间传输信息而言,JSON Web Tokens无疑是一种很好的方式。因为JWTs可以被签名,例如,用公钥/私钥对,你可以确定发送人就是它们所说的那个人。另外,由于签名是使用头和有效负载计算的,所以还可以验证内容没有被篡改。
JWT结构
JWT包含三部分数据:
-
Header:头部,通常头部有两部分信息:
- 声明类型,即token的类型(“JWT”)
- 算法名称(比如:HMAC SHA256或者RSA等等)。
然后,用Base64对这个JSON编码就得到JWT的第一部分
-
Payload:载荷,就是有效数据,一般包含下面信息:
- 用户身份信息(注:这里因为采用base64编码,可解码,因此不要存放敏感信息;除非单独加密)
- 注册声明:如token的签发时间,过期时间,签发人等
这部分也会采用base64编码,得到JWT第二部分数据
-
Signature:签名,是整个数据的认证信息。一般根据前两步的数据,再加上服务的的密钥(secret)(不要泄漏,最好周期性更换),通过加密算法生成。用于验证整个数据完整和可靠性。
生成的数据格式:token==个人证件 jwt=个人身份证
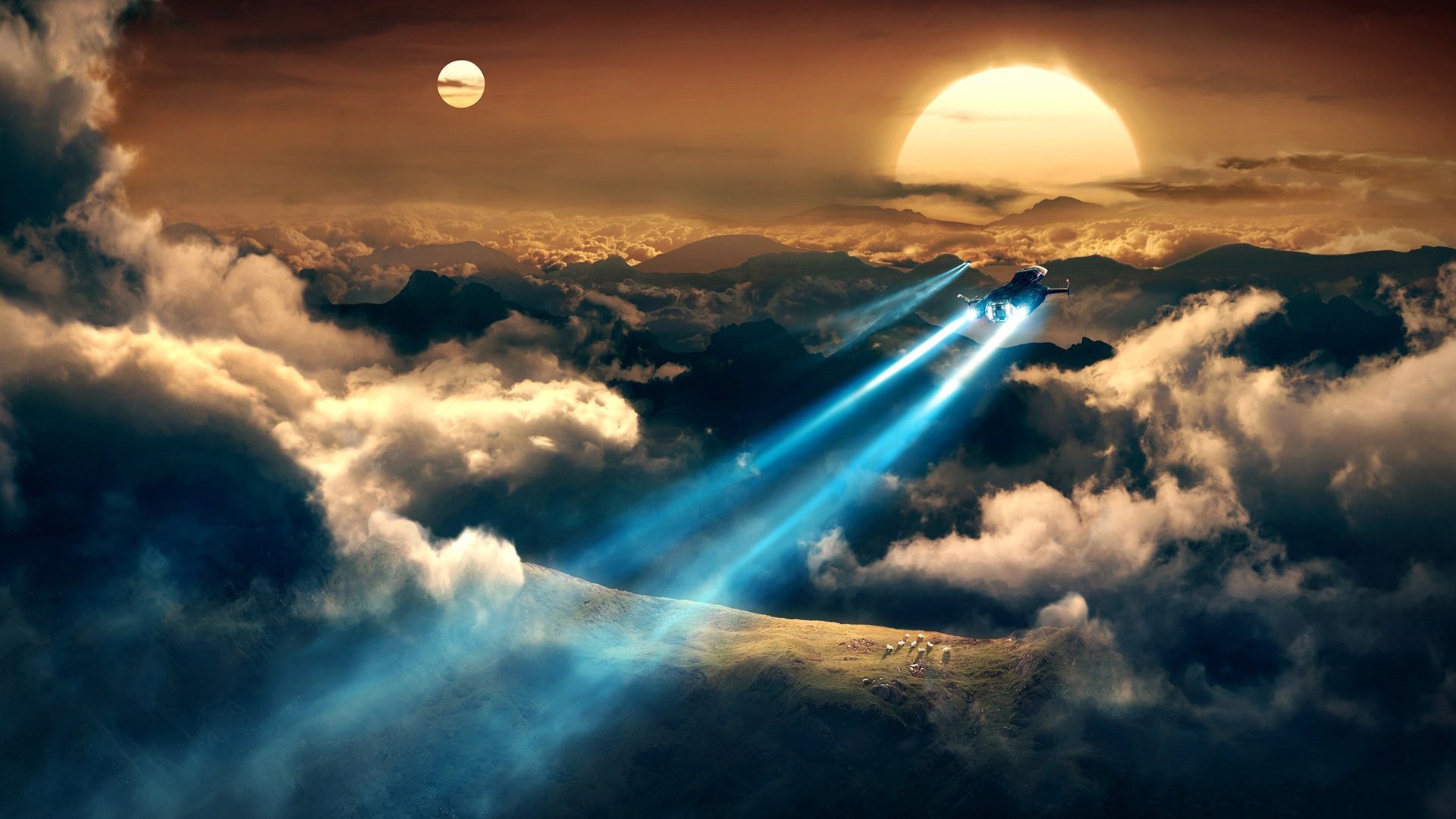
官网案例:
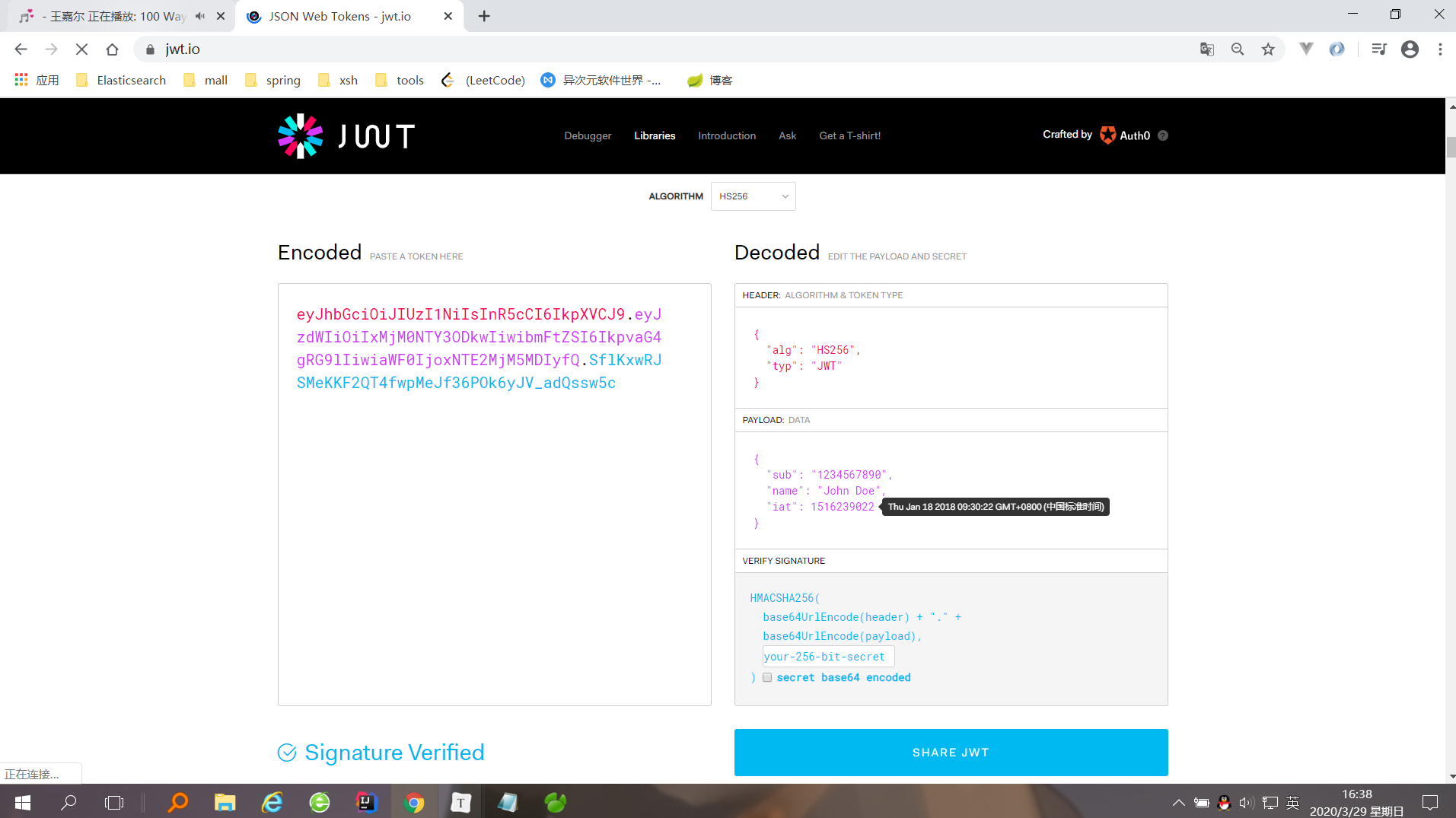
其中Encoded栏下,红色部分为头部Header;紫色部分为载荷;蓝色部分为签名。
二. 有状态登录与无状态登录
2.1 有状态登录
有状态服务,即服务端需要记录每次会话的客户端信息,从而识别客户端身份,根据用户身份进行请求的处理,典型的设计如tomcat中的session。
例如登录:用户登录后,我们把登录者的信息保存在服务端session中,并且给用户一个cookie值,记录对应的session。然后下次请求,用户携带cookie值来,我们就能识别到对应session,从而找到用户的信息。
缺点:
- 服务端保存大量数据,增加服务端压力
- 服务端保存用户状态,无法进行水平扩展
- 客户端请求依赖服务端,多次请求必须访问同一台服务器
2.2 无状态登录
微服务集群中的每个服务,对外提供的都是Rest风格的接口。而Rest风格的一个最重要的规范就是:服务的无状态性,即:
- 服务端不保存任何客户端请求者信息
- 客户端的每次请求必须具备自描述信息,通过这些信息识别客户端身份
带来的好处:
- 客户端请求不依赖服务端的信息,任何多次请求不需要必须访问到同一台服务
- 服务端的集群和状态对客户端透明
- 服务端可以任意的迁移和伸缩
- 减小服务端存储压力
2.3 实现无状态
无状态登录的流程:
- 当客户端第一次请求服务时,服务端对用户进行信息认证(登录)
- 认证通过,将用户信息进行加密形成token,返回给客户端,作为登录凭证
- 以后每次请求,客户端都携带认证的token
- 服务的对token进行解密,判断是否有效。
流程图:
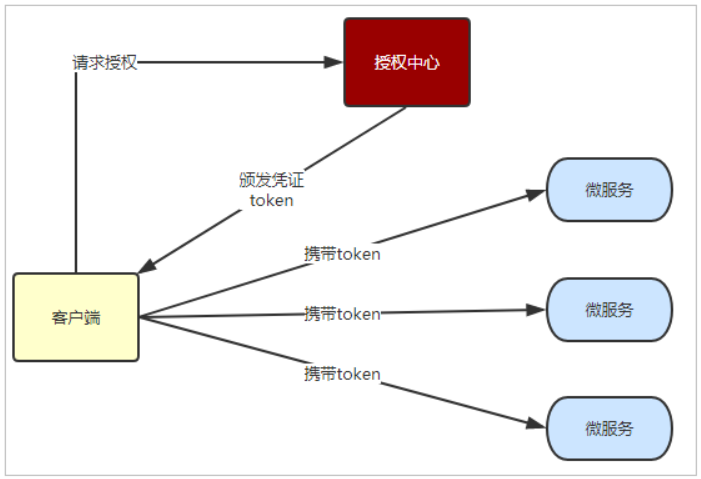
整个登录过程中,最关键的点就是token的安全性!
token是识别客户端身份的唯一标示,如果加密不够严密,被人伪造那就完蛋了。
而采用JWT + RSA非对称加密方式加密能安全可靠。
JWT交互流程:
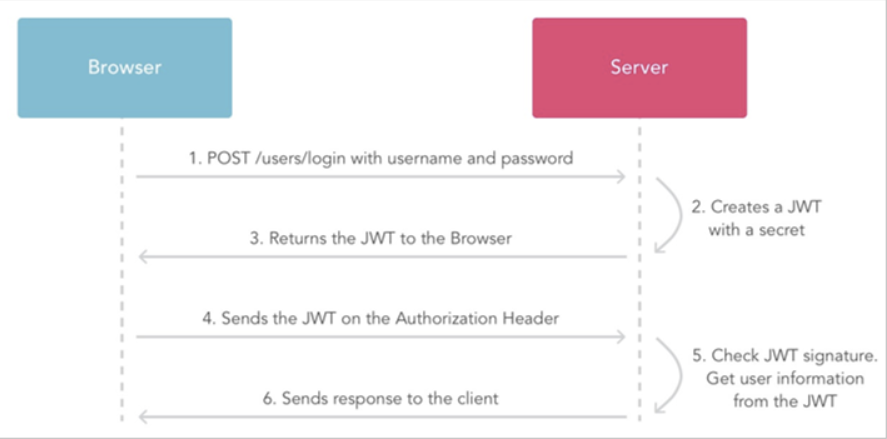
步骤:
- 1、用户登录
- 2、服务的认证,通过后根据secret生成token
- 3、将生成的token返回给浏览器
- 4、用户每次请求携带token
- 5、服务端利用公钥解读jwt签名,判断签名有效后,从Payload中获取用户信息
- 6、处理请求,返回响应结果
因为JWT签发的token中已经包含了用户的身份信息,并且每次请求都会携带,这样服务的就无需保存用户信息,甚至无需去数据库查询,完全符合了Rest的无状态规范。
非对称加密:
加密技术是对信息进行编码和解码的技术,编码是把原来可读信息(又称明文)译成代码形式(又称密文),其逆过程就是解码(解密),加密技术的要点是加密算法,加密算法可以分为三类:
- 对称加密,如AES
- 基本原理:将明文分成N个组,然后使用密钥对各个组进行加密,形成各自的密文,最后把所有的分组密文进行合并,形成最终的密文。
- 优势:算法公开、计算量小、加密速度快、加密效率高
- 缺陷:双方都使用同样密钥,安全性得不到保证
- 非对称加密,如RSA
- 基本原理:同时生成两把密钥:私钥和公钥,私钥隐秘保存,公钥可以下发给信任客户端
- 私钥加密,持有私钥或公钥才可以解密
- 公钥加密,持有私钥才可解密
- 优点:安全,难以破解
- 缺点:算法比较耗时
- 基本原理:同时生成两把密钥:私钥和公钥,私钥隐秘保存,公钥可以下发给信任客户端
- 不可逆加密,如MD5,SHA
- 基本原理:加密过程中不需要使用密钥,输入明文后由系统直接经过加密算法处理成密文,这种加密后的数据是无法被解密的,无法根据密文推算出明文。
RSA算法历史:
1977年,三位数学家Rivest、Shamir 和 Adleman 设计了一种算法,可以实现非对称加密。这种算法用他们三个人的名字缩写:RSA。
三. JWT使用
相关依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt</artifactId>
<version>0.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--对时间处理的工具类,用于设置jwt过期时间-->
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-time</groupId>
<artifactId>joda-time</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--StringUtils依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--用于测试jwt公钥与密钥生成-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3.1 工具类
3.1.1 RsaUtils
package com.xsh.common.utils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.security.*;
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec;
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec;
public class RsaUtils {
/**
* 从文件中读取公钥
*
* @param filename 公钥保存路径,相对于classpath
* @return 公钥对象
* @throws Exception
*/
public static PublicKey getPublicKey(String filename) throws Exception {
byte[] bytes = readFile(filename);
return getPublicKey(bytes);
}
/**
* 从文件中读取密钥
*
* @param filename 私钥保存路径,相对于classpath
* @return 私钥对象
* @throws Exception
*/
public static PrivateKey getPrivateKey(String filename) throws Exception {
byte[] bytes = readFile(filename);
return getPrivateKey(bytes);
}
/**
* 获取公钥
*
* @param bytes 公钥的字节形式
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static PublicKey getPublicKey(byte[] bytes) throws Exception {
X509EncodedKeySpec spec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(bytes);
KeyFactory factory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return factory.generatePublic(spec);
}
/**
* 获取密钥
*
* @param bytes 私钥的字节形式
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static PrivateKey getPrivateKey(byte[] bytes) throws Exception {
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec spec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(bytes);
KeyFactory factory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return factory.generatePrivate(spec);
}
/**
* 根据密文,生存rsa公钥和私钥,并写入指定文件
*
* @param publicKeyFilename 公钥文件路径
* @param privateKeyFilename 私钥文件路径
* @param secret 生成密钥的密文
* @throws IOException
* @throws NoSuchAlgorithmException
*/
public static void generateKey(String publicKeyFilename, String privateKeyFilename, String secret) throws Exception {
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
SecureRandom secureRandom = new SecureRandom(secret.getBytes());
keyPairGenerator.initialize(1024, secureRandom);
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.genKeyPair();
// 获取公钥并写出
byte[] publicKeyBytes = keyPair.getPublic().getEncoded();
writeFile(publicKeyFilename, publicKeyBytes);
// 获取私钥并写出
byte[] privateKeyBytes = keyPair.getPrivate().getEncoded();
writeFile(privateKeyFilename, privateKeyBytes);
}
private static byte[] readFile(String fileName) throws Exception {
return Files.readAllBytes(new File(fileName).toPath());
}
private static void writeFile(String destPath, byte[] bytes) throws IOException {
File dest = new File(destPath);
if (!dest.exists()) {
dest.createNewFile();
}
Files.write(dest.toPath(), bytes);
}
}
3.1.2 ObjectUtils
package com.xsh.common.utils;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
/**
* 从jwt解析得到的数据是Object类型,转换为具体类型可能出现空指针,
* 这个工具类进行了一些转换
*/
public class ObjectUtils {
public static String toString(Object obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return null;
}
return obj.toString();
}
public static Long toLong(Object obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return 0L;
}
if (obj instanceof Double || obj instanceof Float) {
return Long.valueOf(StringUtils.substringBefore(obj.toString(), "."));
}
if (obj instanceof Number) {
return Long.valueOf(obj.toString());
}
if (obj instanceof String) {
return Long.valueOf(obj.toString());
} else {
return 0L;
}
}
public static Integer toInt(Object obj) {
return toLong(obj).intValue();
}
}
3.1.3 JwtUtils
package com.xsh.common.utils;
import com.xsh.common.pojo.UserInfo;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Claims;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jws;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts;
import io.jsonwebtoken.SignatureAlgorithm;
import org.joda.time.DateTime;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
public class JwtUtils {
/**
* 私钥加密token
*
* @param userInfo 载荷中的数据
* @param privateKey 私钥
* @param expireMinutes 过期时间,单位秒
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static String generateToken(UserInfo userInfo, PrivateKey privateKey, int expireMinutes) throws Exception {
return Jwts.builder()
.claim(JwtConstans.JWT_KEY_ID, userInfo.getId())
.claim(JwtConstans.JWT_KEY_USER_NAME, userInfo.getUsername())
.setExpiration(DateTime.now().plusMinutes(expireMinutes).toDate())
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.RS256, privateKey)
.compact();
}
/**
* 私钥加密token
*
* @param userInfo 载荷中的数据
* @param privateKey 私钥字节数组
* @param expireMinutes 过期时间,单位秒
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static String generateToken(UserInfo userInfo, byte[] privateKey, int expireMinutes) throws Exception {
return Jwts.builder()
.claim(JwtConstans.JWT_KEY_ID, userInfo.getId())
.claim(JwtConstans.JWT_KEY_USER_NAME, userInfo.getUsername())
.setExpiration(DateTime.now().plusMinutes(expireMinutes).toDate())
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.RS256, RsaUtils.getPrivateKey(privateKey))
.compact();
}
/**
* 公钥解析token
*
* @param token 用户请求中的token
* @param publicKey 公钥
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private static Jws<Claims> parserToken(String token, PublicKey publicKey) {
return Jwts.parser().setSigningKey(publicKey).parseClaimsJws(token);
}
/**
* 公钥解析token
*
* @param token 用户请求中的token
* @param publicKey 公钥字节数组
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private static Jws<Claims> parserToken(String token, byte[] publicKey) throws Exception {
return Jwts.parser().setSigningKey(RsaUtils.getPublicKey(publicKey))
.parseClaimsJws(token);
}
/**
* 获取token中的用户信息
*
* @param token 用户请求中的令牌
* @param publicKey 公钥
* @return 用户信息
* @throws Exception
*/
public static UserInfo getInfoFromToken(String token, PublicKey publicKey) throws Exception {
Jws<Claims> claimsJws = parserToken(token, publicKey);
Claims body = claimsJws.getBody();
return new UserInfo(
ObjectUtils.toLong(body.get(JwtConstans.JWT_KEY_ID)),
ObjectUtils.toString(body.get(JwtConstans.JWT_KEY_USER_NAME))
);
}
/**
* 获取token中的用户信息
*
* @param token 用户请求中的令牌
* @param publicKey 公钥
* @return 用户信息
* @throws Exception
*/
public static UserInfo getInfoFromToken(String token, byte[] publicKey) throws Exception {
Jws<Claims> claimsJws = parserToken(token, publicKey);
Claims body = claimsJws.getBody();
return new UserInfo(
ObjectUtils.toLong(body.get(JwtConstans.JWT_KEY_ID)),
ObjectUtils.toString(body.get(JwtConstans.JWT_KEY_USER_NAME))
);
}
}
3.1.4 JwtConstans
package com.xsh.common.utils;
public abstract class JwtConstans {
public static final String JWT_KEY_ID = "id";
public static final String JWT_KEY_USER_NAME = "username";
}
3.2 pojo
package com.xsh.common.pojo;
/**
* 载荷对象,即传输的有效数据,此处只传id和用户名
*/
public class UserInfo {
private Long id;
private String username;
public UserInfo() {
}
public UserInfo(Long id, String username) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
}
public Long getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
}
3.3 JwtTest
package com.xsh.auth.test;
import com.xshxshxsh.common.pojo.UserInfo;
import com.xshxsh.common.utils.JwtUtils;
import com.xsh.common.utils.RsaUtils;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
/**
* @author : xsh
* @create : 2020-03-29 - 15:13
* @describe:
*/
public class JwtTest {
/*定义保存公钥与密钥的路径*/
private static final String basicPath ="E:\\test_Jwt\\";
private static final String pubKeyPath = basicPath+"rsa.pub";//公钥路径
private static final String priKeyPath = basicPath+"rsa.pri";//私钥路径
private PublicKey publicKey;
private PrivateKey privateKey;
/**
* 在指定路径生成公钥和私钥
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testRsa() throws Exception {
RsaUtils.generateKey(pubKeyPath, priKeyPath, "xsh");//secret为加密盐,实际使用时应越复杂越好,数字+字母+字符组合
}
/**
* 读取公钥和私钥。当没有公钥和私钥时,即第一次运行测试,应先注释掉@Before再运行testRsa()方法生成公钥和私钥,然后取消注释运行其它方法
* @throws Exception
*/
@Before
public void testGetRsa() throws Exception {
this.publicKey = RsaUtils.getPublicKey(pubKeyPath);
this.privateKey = RsaUtils.getPrivateKey(priKeyPath);
}
@Test
public void testGenerateToken() throws Exception {
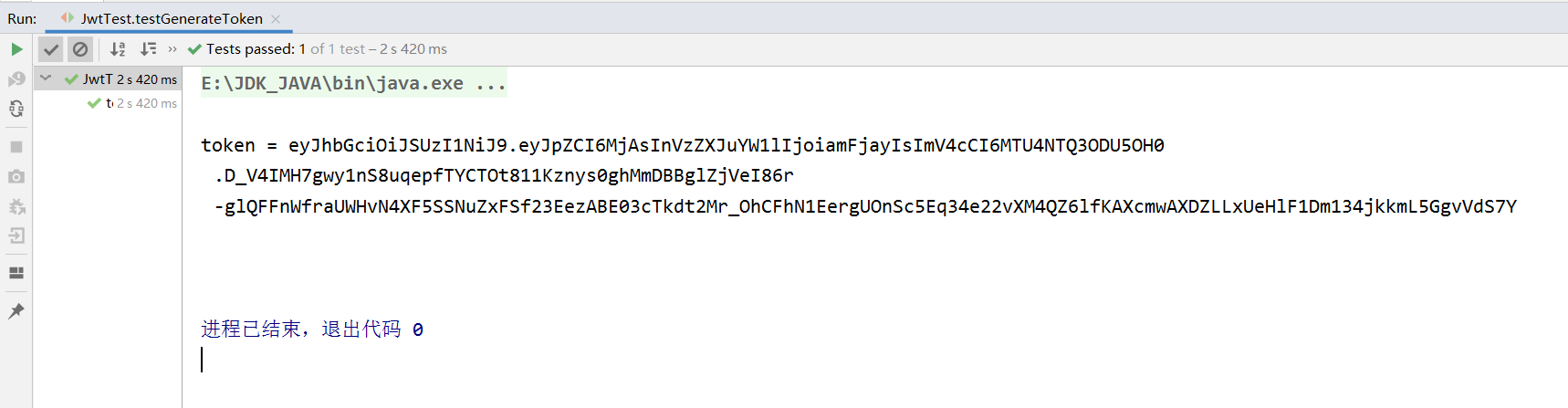
// 使用私钥生成token,定义过期时间为5分钟,传输信息id=21,username=xsh
String token = JwtUtils.generateToken(new UserInfo(21L, "xsh"), privateKey, 5);
System.out.println("token = " + token);
}
@Test
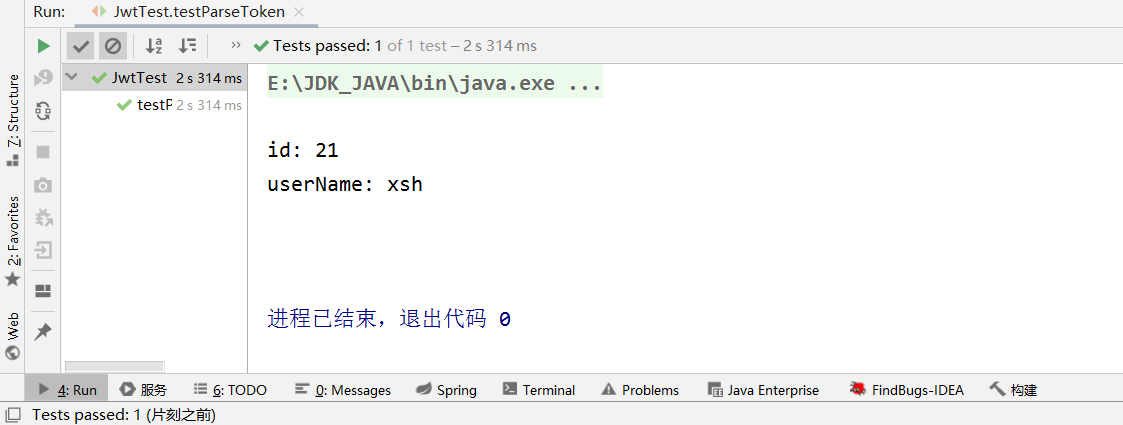
public void testParseToken() throws Exception {
//token不固定且5分钟过期,需运行testGenerateToken()方法后进行替换
String token = "eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJpZCI6MjAsInVzZXJuYW1lIjoiamFjayIsImV4cCI6MTU4MDk3MTAyMX0.SK_uYdDzTiHtIk3g0eTdVV9S4i8IyDA_oJ2VktksogmrSL9FmRRykWghakDuFrzNut2nt5zAt1h56vgkj1Y18iB_69Kz2YfkEpZatztlhwn3Wc2GoHLeiuS6Yp3kcyrY1dUQVcUHNOf_StAprOgLDBCBbo3ZDL1uUc0r9-RQqiU";
// 使用公钥解析token
UserInfo user = JwtUtils.getInfoFromToken(token, publicKey);
System.out.println("id: " + user.getId());
System.out.println("userName: " + user.getUsername());
}
}
运行testRsa()方法,会在指定路径生成公钥和私钥文件:
运行testGenerateToken()方法生成token携带信息并设置过期时间:
将token复制到testParseToken()方法内并运行,当token在有效期内,既可解析token内的信息:
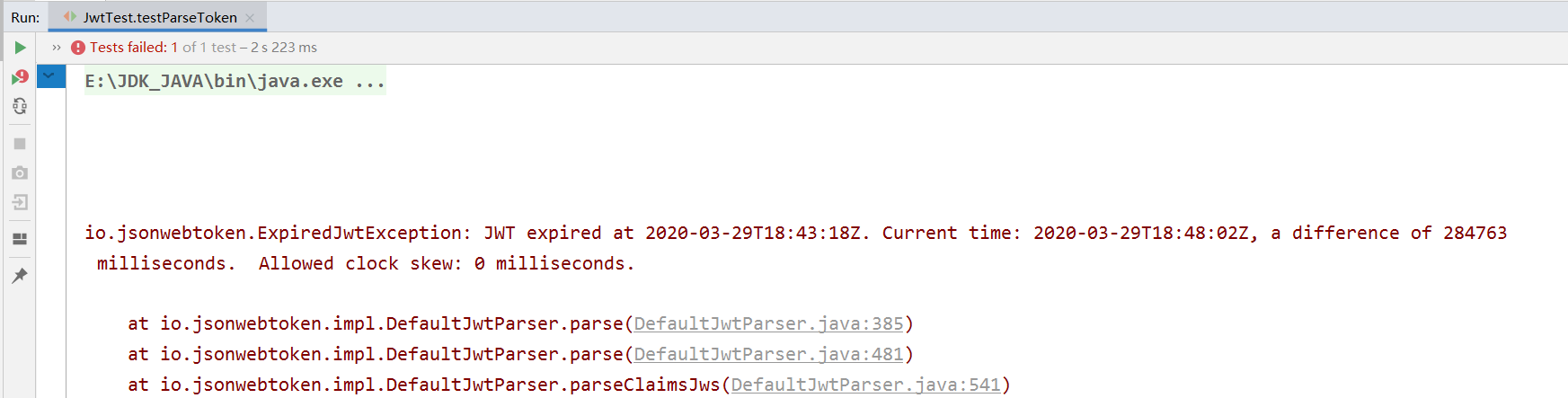
当token过期时再解析信息时会抛出异常:
3.4 使用JWT完成登录案例
3.4.1 AuthService
package com.xsh.auth.service;
import com.xsh.auth.client.UserClient;
import com.xsh.auth.config.JwtProperties;
import com.xsh.common.pojo.UserInfo;
import com.xsh.common.utils.JwtUtils;
import com.xsh.user.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author : xsh
* @create : 2020-03-29 - 18:04
* @describe:
*/
@Service
public class AuthService {
@Autowired
private UserClient userClient;
@Autowired
private JwtProperties jwtProperties;
public String accredit(String username, String password) {
//1.根据用户名和密码查询
User user = this.userClient.queryUser(username, password);
//2.判断user
if(user == null){
return null;
}
//3.jwtUtils生成jwt类型的token
try {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setId(user.getId());
userInfo.setUsername(user.getUsername());
return JwtUtils.generateToken(userInfo,this.jwtProperties.getPrivateKey(),this.jwtProperties.getExpire());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
3.4.2 AuthController
package com.xsh.auth.controller;
/**
* @author : xsh
* @create : 2020-03-29 - 18:34
* @describe:
*/
@Controller
@EnableConfigurationProperties(JwtProperties.class)
public class AuthController {
@Autowired
private AuthService authService;
@Autowired
private JwtProperties jwtProperties;
@PostMapping("accredit")
public ResponseEntity<Void> accredit(@RequestParam("username")String username,
@RequestParam("password")String password,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response){
String token = this.authService.accredit(username,password);
if(StringUtils.isBlank(token)){
//return ResponseEntity.badRequest().build();
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED).build();//身份未认证错误
}
//因为配置文件过期时间单位为分钟,而工具类中单位为秒,所以需要*60
CookieUtils.setCookie(request,response,this.jwtProperties.getCookieName(),token,this.jwtProperties.getExpire()*60);
return ResponseEntity.ok(null);
}
@GetMapping("verify")
public ResponseEntity<UserInfo> verify(@CookieValue("XSH_TOKEN") String token,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response){
try {
//通过jwt工具类,使用公钥解析出载荷信息
UserInfo user = JwtUtils.getInfoFromToken(token, this.jwtProperties.getPublicKey());
if(user == null){
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED).build();
}
/**
* cookie和jwt设置为30分钟有效,30分钟用户不操作则登录生效,当用户在操作时则需要刷新有效时间
*/
//刷新jwt中有效时间(无刷新方法,重新生成一个新的)
token=JwtUtils.generateToken(user,this.jwtProperties.getPrivateKey(),this.jwtProperties.getExpire());
//刷新cookie中的有效时间(无刷新方法,重新生成一个新的)
CookieUtils.setCookie(request,response,this.jwtProperties.getCookieName(),token,this.jwtProperties.getExpire()*60);
return ResponseEntity.ok(user);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED).build();
}
}
3.4.3 JwtProperties
package com.xsh.auth.config;
import com.xsh.common.utils.RsaUtils;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.io.File;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "xsh.jwt")
public class JwtProperties {
private String secret; // 密钥
private String pubKeyPath;// 公钥
private String priKeyPath;// 私钥
private int expire;// token过期时间
private String cookieName;
private PublicKey publicKey; // 公钥
private PrivateKey privateKey; // 私钥
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JwtProperties.class);
/**
* @PostContruct:在构造方法执行之后执行该方法
*/
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
try {
File pubKey = new File(pubKeyPath);
File priKey = new File(priKeyPath);
if (!pubKey.exists() || !priKey.exists()) {
// 生成公钥和私钥
RsaUtils.generateKey(pubKeyPath, priKeyPath, secret);
}
// 获取公钥和私钥
this.publicKey = RsaUtils.getPublicKey(pubKeyPath);
this.privateKey = RsaUtils.getPrivateKey(priKeyPath);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("初始化公钥和私钥失败!", e);
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
//此处还需加入setter和getter方法,已省略。
}
3.4.4 yml配置文件
xsh:
jwt:
secret: xsh@Login(Auth}*^22)&xsh% # 登录校验的密钥,越复杂越好
pubKeyPath: E:\\学习\\rsa.pub # 公钥地址
priKeyPath: E:\\学习\\rsa.pri # 私钥地址
expire: 30 # 过期时间,单位分钟
cookieName: XSH_TOKEN
客户端接收服务器返回的JWT,将其存储在Cookie或localStorage中。
此后,客户端将在与服务器交互中都会带JWT。如果将它存储在Cookie中,就可以自动发送,但是不会跨域,因此一般是将它放入HTTP请求的Header Authorization字段中。
Authorization: Bearer
当跨域时,也可以将JWT被放置于POST请求的数据主体中。
四. JWT与Session区别
- 相同点是,它们都是存储用户信息;然而,Session是在服务器端的,而JWT是在客户端的。
- Session方式存储用户信息的最大问题在于要占用大量服务器内存,增加服务器的开销。而JWT方式将用户状态分散到了客户端中,可以明显减轻服务端的内存压力。
- Session的状态是存储在服务器端,客户端只有session id;而Token的状态是存储在客户端。
4.1 基于服务器的身份认证
HTTP协议是无状态的,也就是说,如果我们已经认证了一个用户,那么他下一次请求的时候,服务器不知道我是谁,我们必须再次认证
传统的做法是将已经认证过的用户信息存储在服务器上,比如Session。用户下次请求的时候带着Session ID,然后服务器以此检查用户是否认证过。
这种基于服务器的身份认证方式存在一些问题:
- Sessions : 每次用户认证通过以后,服务器需要创建一条记录保存用户信息,通常是在内存中,随着认证通过的用户越来越多,服务器的在这里的开销就会越来越大。
- Scalability : 由于Session是在内存中的,这就带来一些扩展性的问题。
- CORS : 当我们想要扩展我们的应用,让我们的数据被多个移动设备使用时,我们必须考虑跨资源共享问题。当使用AJAX调用从另一个域名下获取资源时,我们可能会遇到禁止请求的问题。
- CSRF : 用户很容易受到CSRF攻击。
4.2 基于Token的身份认证
基于Token的身份认证是无状态的,服务器或者Session中不会存储任何用户信息。
没有会话信息意味着应用程序可以根据需要扩展和添加更多的机器,而不必担心用户登录的位置。
虽然这一实现可能会有所不同,但其主要流程如下:
- 用户携带用户名和密码请求访问
- 服务器校验用户凭据
- 应用提供一个token给客户端
- 客户端存储token,并且在随后的每一次请求中都带着它
- 服务器校验token并返回数据
注意:
- 每一次请求都需要token
- Token应该放在请求header中
- 我们还需要将服务器设置为接受来自所有域的请求,用Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
4.3 用Token的好处
-
无状态和可扩展性:Tokens存储在客户端。完全无状态,可扩展。负载均衡器可以将用户传递到任意服务器,因为在任何地方都没有状态或会话信息。
-
安全:Token不是Cookie。(The token, not a cookie.)每次请求的时候Token都会被发送。而且,由于没有Cookie被发送,还有助于防止CSRF攻击。即使在你的实现中将token存储到客户端的Cookie中,这个Cookie也只是一种存储机制,而非身份认证机制。没有基于会话的信息可以操作,因为没有会话!
-
token在一段时间以后会过期,这个时候用户需要重新登录。这有助于保持安全。还有一个概念叫token撤销,它允许根据相同的授权许可使特定的token甚至一组token无效。
4.4 JWT与OAuth的区别
- OAuth2是一种授权框架 ,JWT是一种认证协议
- 无论使用哪种方式切记用HTTPS来保证数据的安全性
- OAuth2用在使用第三方账号登录的情况(比如使用weibo, qq, github登录某个app),而JWT是用在前后端分离, 需要简单的对后台API进行保护时使用.
五. JWT问题和趋势
1、JWT默认不加密,但可以加密。生成原始令牌后,可以使用改令牌再次对其进行加密。
2、当JWT未加密方法时,一些私密数据无法通过JWT传输。
3、JWT不仅可用于认证,还可用于信息交换。善用JWT有助于减少服务器请求数据库的次数。
4、JWT的最大缺点是服务器不保存会话状态,所以在使用期间不可能取消令牌或更改令牌的权限。也就是说,一旦JWT签发,在有效期内将会一直有效。
5、JWT本身包含认证信息,因此一旦信息泄露,任何人都可以获得令牌的所有权限。为了减少盗用,JWT的有效期不宜设置太长。对于某些重要操作,用户在使用时应该每次都进行进行身份验证。
6、为了减少盗用和窃取,JWT不建议使用HTTP协议来传输代码,而是使用加密的HTTPS协议进行传输。

评论